|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
Archive Advocate
Works Of Art 2017
5x7" 8.5x11" 6 Parts Truth Portraits Time Eye
Eye
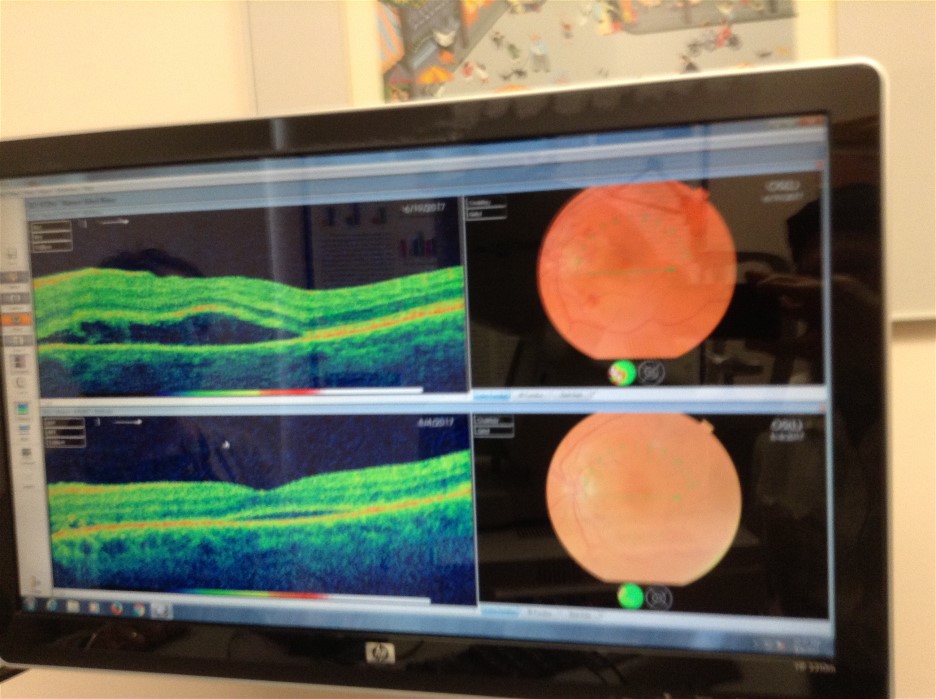
Graph of Retina distortion - 2017 -
|
What is AMD? Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a progressive eye condition that damages the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. There are two forms of AMD, dry and wet. About 90% of people diagnosed with AMD have dry AMD. Early AMD always starts out as dry, but in about 10% of cases it can develop into wet AMD. Wet AMD Wet AMD occurs when delicate, abnormal blood vessels form under the retina. These new blood vessels tend to be very fragile and often leak blood and fluid, causing the retina to distort or scar. Damage to the macula occurs rapidly. With wet AMD, loss of central vision can occur quickly. Your doctor can recommend interventions to help limit your vision loss due to wet AMD. Common Symptoms of Wet AMD: 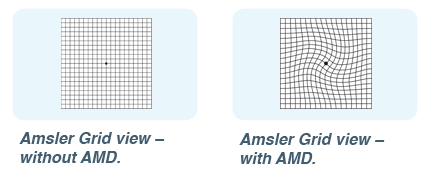 Graph of Retina distortion Straight Lines Appear Crooked: When fluid from leaking blood vessels gathers and lifts the macula, it can distort your vision and make straight lines – like door frames – appear bent or crooked. With AMD Non-Seeing Areas in Central Vision: If the loss of these light-sensing cells becomes great, you may notice small – but growing – non-seeing areas or scotomas in the center of your vision. River has Wet AMD in the left eye. He is under treatment to slow the progression. |
© 1987 - 2025 Glen River Publications, all rights reserved